.svg)
.svg)
.svg)
.svg)
.svg)
.svg)
.svg)
.svg)
.svg)
.svg)
.svg)
.svg)
.svg)
Simple Orders Explained: Speed, Risks & Precision Tools
Understanding the nuances of order types is crucial for navigating price fluctuations and executing successful strategies. Among the fundamental order types, the market order stands out for its promise of immediate execution at the prevailing market price.
This article delves into the mechanics of market orders, exploring their advantages and disadvantages and illustrating their practical application through examples like scalping.
Furthermore, it highlights how advanced trading platforms, such as Altrady, equip traders with sophisticated tools to enhance control and management when utilizing market orders in their trading endeavors.
Understanding the Crypto Trading Market
If you have ever wondered about the forces that influence the price movements of an asset, understanding market orders can disperse any doubt. Supply and demand are one of the elementary concepts behind such movements, and the way traders place orders determines their impact on prices.
The order book is another factor to consider when grasping the market. Assets prices move according to order execution on it and their sizes. Typically, depending on the order size, traders decide whether to use market orders or another type, like a limit order. Why? Let's point out some considerations:
- When using a market order, a trading idea executes instantly at the current price the market moves. This is useful when traders want to enter or exit the market rapidly amid volatile price changes.
- When traders want to average an entire position, distributing the total order in small sizes would be more appropriate. In this case, traders use limit orders to specify the prices at which they want to enter.
It is noteworthy to mention that market orders are the order type behind stop-loss levels and take-profit targets, which heavily impact asset prices, hence the market movements. For example:
- During selloff events, it is said that the market liquidated lots of stop-loss orders. Similarly, during effective upside breakouts.
- During pullbacks or notable retracements, it is said that traders close their positions by taking profits, so the underlying trend slows down.
Example of Trading Market Orders
Scalping
Scalping is a principal example of trading with market orders. It is so because this trading style involves quick entry and exit executions. Scalpers may employ this order type in the following ways:
- Entering manually
- Placing a stop-market order.
Entering Manually
Imagine a breakout scenario where you identify a reversal pattern like a shooting star (uptrend to downtrend) or a morning star (downtrend to uptrend). These patterns consist of breaking a previous candle’s high/low. Entering manually would be as follows:
- You identify one of the patterns (let’s say a morning star) in a higher timeframe, such as 15min, which implies a significant movement in a lower timeframe, such as 3min or 2min.
- Then, you can execute a market order as long as the price crosses the prior candle’s high in the higher timeframe.
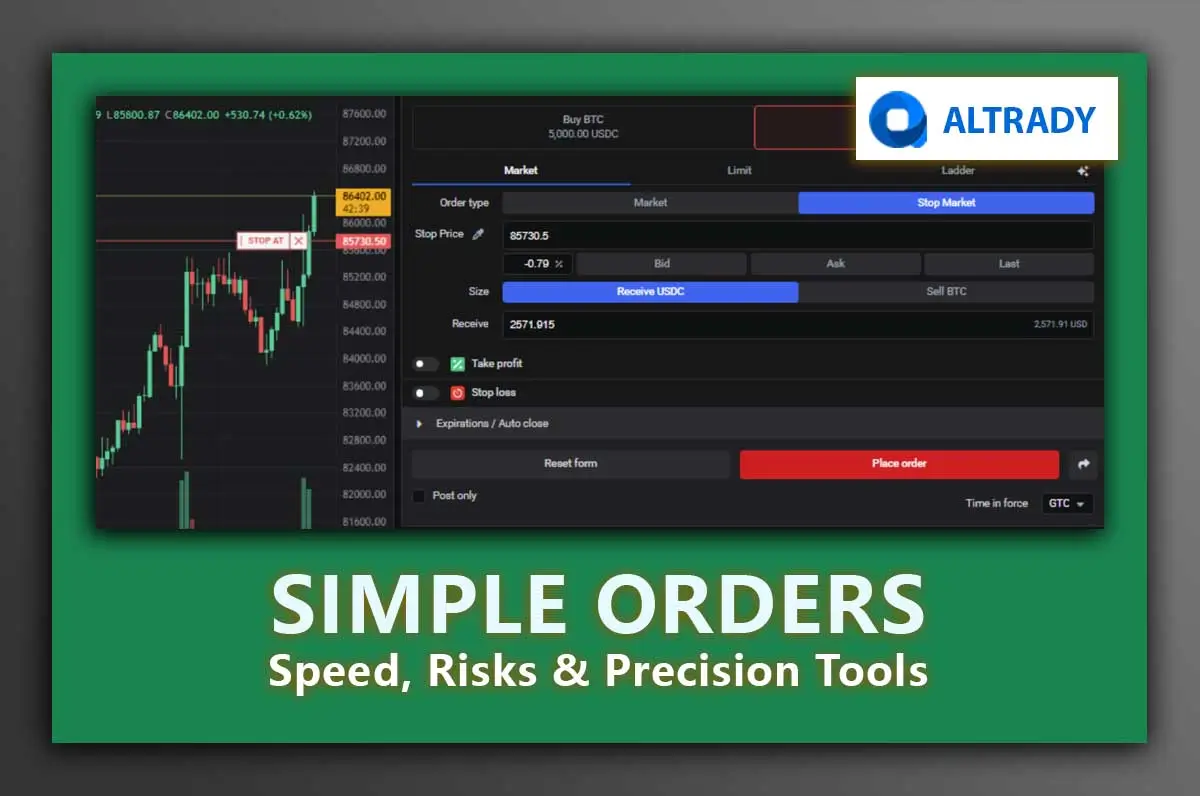
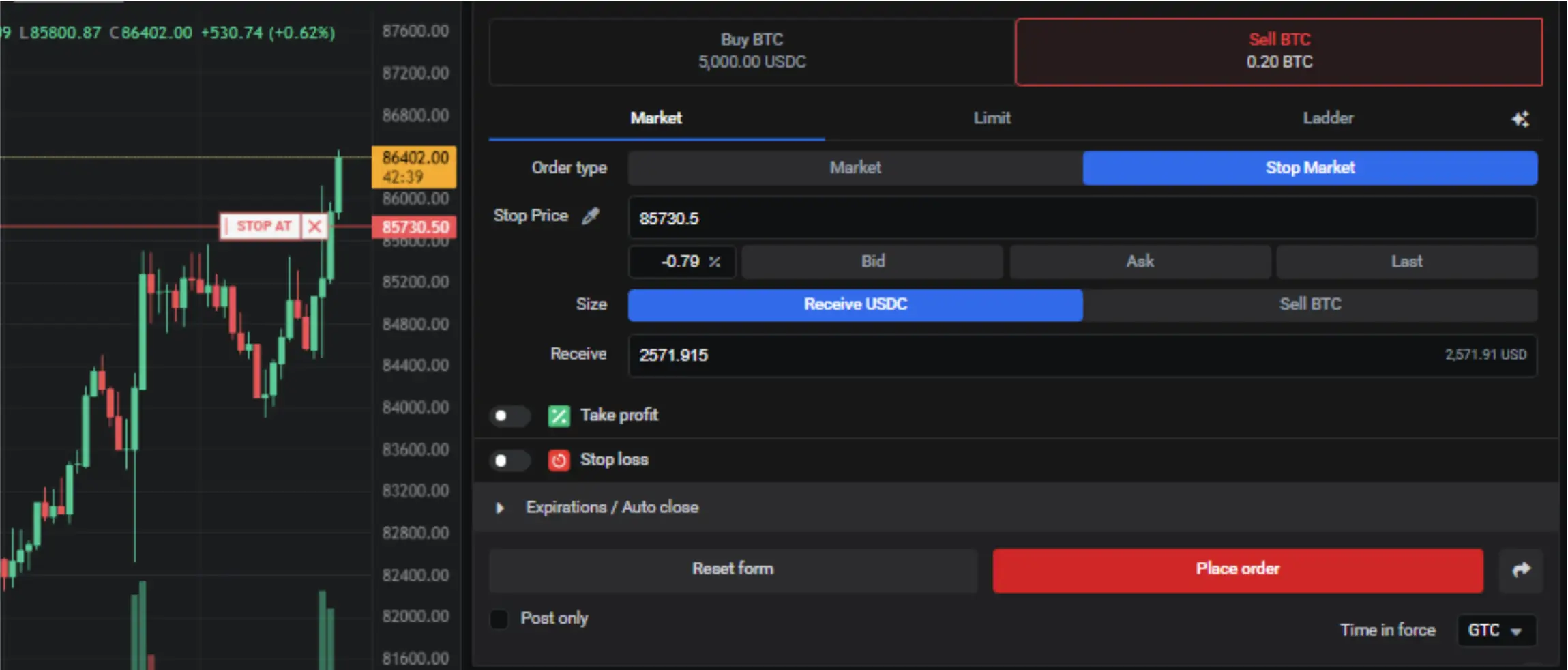
Placing a Stop-market Order
Stop-market orders should not be compared to stop-loss orders. Stop-market is a market order type that executes entries instantly but at a specific price level, similar to limit orders but regardless of the quantity filled.
Now, using the previous breakout scenario as an example, entering with a stop-market order would be as follows:
- You identify one of the patterns (let’s say a shooting star), again in a higher timeframe, 15min, but as a scalper, you look for entries in a lower time frame, 2min.
- In this case, you place a stop-market order that will execute the entry as long as the price crosses the prior candle’s low in the higher timeframe.
A key aspect to remark about stop-market orders is that traders can not place them contrary to the side of execution. For instance:
- If you go upside, you can not place them below the current market price.
- Conversely, if you expect a downside movement, you cannot place them above the market price
- This aspect makes them different from limit orders.
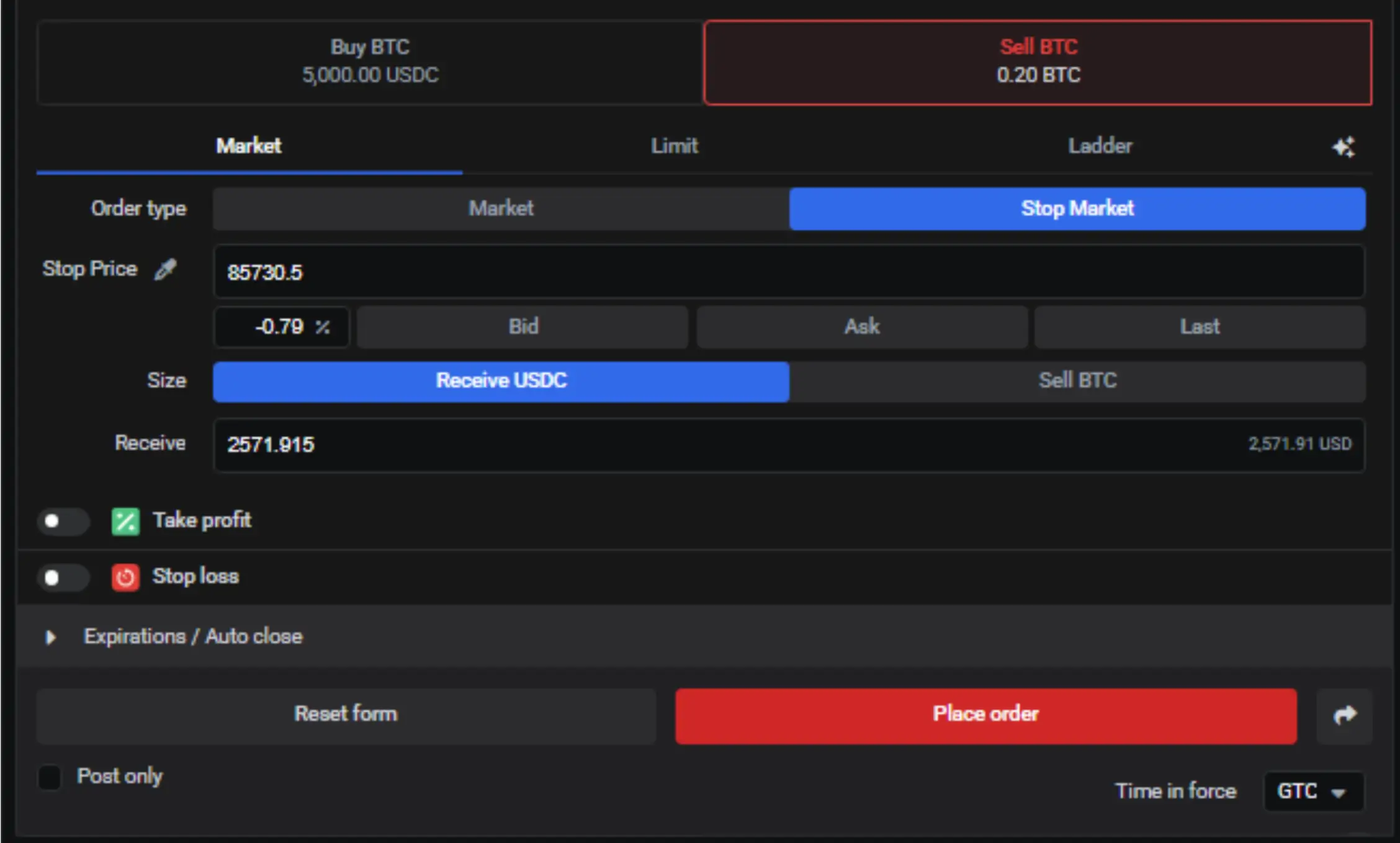
Advantages of Market Orders
- Rapid execution: Market orders execute trades at current market prices. As long as there are buyers and sellers at a specific price, it prioritizes executing trades rapidly.
- More control over the trade execution: Either using a market order or its variant (stop-market), traders constantly monitor the market while they expect execution. During highly volatile markets, this control over execution can be beneficial to enter and exit rapidly. However, there could be some drawbacks.
Disadvantages of Market Orders
- Opportunity costs: Given the fast execution, traders may incur errors when executing trades prematurely. For instance, they may fall in a false breakout movement.
- Less control over the execution price: Unlike limit orders, which may not be executed until they are filled at a specific price, market orders are executed at current prices that may change so rapidly that the trade enters the market at undesirable price levels.
Using Market Orders in Altrady
Altrady’s Smart Trading tools give you additional control over market orders for both execution and management. With these tools, traders of any skill level can benefit from:
- Using stop-market orders in any direction.
- Using multiple take-profit targets.
- Using protection for stop-loss orders.
- Trailing stop-loss.
The Bottom Line
Essentially, a market order is suitable for scenarios where speed and immediate execution are paramount, but they come at the cost of price control. It also exposes traders to risks of slippage in highly volatile market conditions.
A stop-market order is a type of trading order that combines the features of a stop order and a market order. This is a conditional market order designed to trigger a market order when the price reaches a specific price level.
Conclusion
In essence, the market order serves as a vital tool in a trader's arsenal, particularly when swift entry or exit from the market is paramount. While its strength lies in rapid execution, this comes with the inherent trade-off of less control over the final price and potential exposure to slippage, especially in volatile conditions.
However, with the advent of advanced trading platforms like Altrady, traders can leverage sophisticated features to mitigate some of these drawbacks, gaining greater control over their market order execution and management. Start leveraging the benefits of market orders with Altrady’s free trial account with paper trading






























